 Law of Sines
Law of Sines
The Law of Sines states that, in any triangle, the ratio of the sine of an angle to the length of its opposite side is constant. It is a valuable tool in solving triangles.
Solving a Triangle
To solve a triangle means to find all the angles and all the side lengths.
To start, you must be given enough information to uniquely identify the triangle. The triangle congruence theorems (ASA, AAS, SAS, SSS) specify minimal required information. (Be careful! Recall that SSA doesn't work!)
For example, suppose you know two sides of a triangle and an included angle. By SAS, the triangle is then uniquely determined. To ‘solve’ the triangle means to find the remaining side and the remaining two angles.
You already have some of the basic tools useful in solving triangles:
- the sum of the angles in any triangle is $\,180^\circ$
- the right triangle definitions of the trigonometric functions
- the Pythagorean Theorem
To be able to solve any triangle, however, you need the following additional tools:
- the Law of Sines (this section)
- the Law of Cosines (a future section)
- the inverse trigonometric functions (a future section)
The Law of Sines
To motivate the Law of Sines, first consider a right triangle (see below).
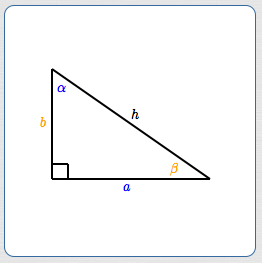
Notice that:
- the side of length $\,\color{blue}{a}\,$ is opposite angle $\,\color{blue}{\alpha}$
- the side of length $\,\color{orange}{b}\,$ is opposite angle $\,\color{orange}{\beta}$
- the side of length $\,h\,$ is opposite the $\,90^\circ\,$ angle
Using the right triangle definition of sine, we have both:
$$ \begin{gather} \cssId{s33}{\sin\alpha = \frac{a}{h} = a\cdot\color{red}{\frac{1}{h}}}\cr\cr \cssId{s34}{\text{and}}\cr\cr \cssId{s35}{\sin\beta = \frac{b}{h} = b\cdot\color{red}{\frac{1}{h}}} \end{gather} $$Solving for $\displaystyle\,\color{red}{\frac{1}{h}}\,$ in both equations, we get:
$$\cssId{s37}{\frac{1}{h} = \frac{\sin\alpha}{a} = \frac{\sin\beta}{b}}$$Since $\,\sin 90^\circ = 1\,,$ we can further write this as:
$$\cssId{s39}{\frac{\sin 90^\circ}{h} = \frac{\sin\alpha}{a} = \frac{\sin\beta}{b}}$$This is an interesting result: the ratio of the sine of an angle to the length of its opposite side is constant!
Is this just a curious result for right triangles, or is it always true? The Law of Sines tells us that it is always true!
Consider an arbitrary triangle (see below), where:
- angle $\,D\,$ is opposite a side of length $\,d\,$
- angle $\,E\,$ is opposite a side of length $\,e\,$
- angle $\,F\,$ is opposite a side of length $\,f\,$
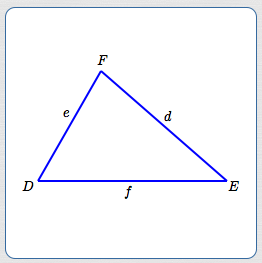
Then:
$$\cssId{s51}{\frac{\sin D}{d} \ =\ \frac{\sin E}{e} \ =\ \frac{\sin F}{f}}$$In words:
Notes on the Law of Sines
Equivalent Statement of the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines can equivalently be stated as:
$$ \cssId{s56}{\frac{d}{\sin D} \ =\ \frac{e}{\sin E} \ =\ \frac{f}{\sin F}} $$No Worries about Zero in the Denominator
Since lengths of sides in triangles are strictly positive, $\,d\,,$ $\,e\,,$ and $\,f\,$ are always nonzero.
Since angles in triangles are never $\,0^\circ\,$ or $\,180^\circ\,,$ $\,\sin D\,,$ $\,\sin E\,,$ and $\,\sin F\,$ are always nonzero.
Avoid Using $\,C\,$ and $\,c\,$ to Denote an Angle/Side Pair
Since uppercase $\,C\,$ and lowercase $\,c\,$ look so similar, avoid using these variables to denote an ‘angle/opposite side’ pair.
What is Needed to Use the Law of Sines?
To use the Law of Sines to solve a triangle, you must know an angle and its opposite side.
For example, the Law of Sines cannot be used (as a first step) to solve a SSS triangle, since you don't initially know an angle and its opposite side.
Notational Abuse
Observe that a vertex of a triangle uniquely identifies the angle at that vertex. Thus, you can think of (say) $\,D\,$ as a vertex of a triangle (a point)—or, as the angle at that vertex.
For ease of notation, people often do not use two different variables for the vertex and the angle at that vertex, instead relying on context to determine intent.
Thus, you may see ‘$\,\sin D\,$’, where $\,D\,$ is being viewed as (the measure of) an angle.
You may also see ‘$\,\triangle DEF\,$’, where $\,D\,$ is being viewed as a point.
This sort of ‘notational duplicity’ is fine in contexts where there is no possible confusion.
Proof of the Law of Sines
The proof of the Law of Sines is an immediate consequence of the area formula for a triangle, given two sides and an included angle :
Use the notation above, where angles $\,D\,,$ $\,E\,,$ and $\,F\,$ have opposite sides (respectively) $\,d\,,$ $\,e\,,$ and $\,f\,.$

- Use sides $\,e\,$ and $\,f\,$ to find the area: $$ \cssId{s74}{\text{Area} = \frac 12ef\sin D} $$
- Use sides $\,d\,$ and $\,f\,$ to find the area: $$\cssId{s76}{\text{Area} = \frac 12df\sin E}$$
- Use sides $\,d\,$ and $\,e\,$ to find the area: $$\cssId{s78}{\text{Area} = \frac 12de\sin F}$$
Consequently, we have:
Multiply through by $\displaystyle\,\frac 2{def}\,$:
$$ \cssId{s82}{\frac{\sin D}{d} \ =\ \frac{\sin E}{e} \ =\ \frac{\sin F}{f}} $$Voila! Such a powerful result with such a simple proof!
Example: Using the Law of Sines
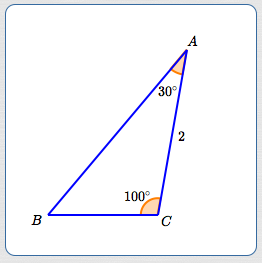
Consider a triangle with angles $\,30^\circ\,$ and $\,100^\circ\,,$ and an enclosed side of length $\,2\,.$
Prove that this information uniquely defines a triangle, and then solve the triangle. Give exact solutions, and then approximate (as needed) to three decimal places.
Solution
By ASA, the triangle is unique. The notation below is used in the solution.

The notation ‘$\,AB\,$’ is used to denote the length of the side from $\,A\,$ to $\,B\,.$
- $\,B = 180^\circ - 30^\circ - 100^\circ = 50^\circ\,$
- By the Law of Sines: $$ \cssId{s94}{\frac{\sin 50^\circ}{2} = \frac{\sin 30^\circ}{BC} = \frac{\sin 100^\circ}{AB}} $$
- Thus: $$ \begin{gather} \cssId{s96}{BC = \frac{2\sin 30^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ} \approx 1.305}\cr\cr\cr \cssId{s97}{AB = \frac{2\sin 100^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ} \approx 2.571} \end{gather} $$